Astm d698 vs astm d1557 – ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 stand as prominent materials in various industries, each boasting unique properties and applications. Embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of these materials, comparing their properties, manufacturing processes, and performance characteristics.
As we delve into the world of ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557, we’ll uncover their strengths and limitations, empowering you to make informed decisions in your material selection process.
Properties and Applications
ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 are two standard test methods for determining the properties of plastics. While both methods can be used to evaluate a variety of plastic materials, there are some key differences between the two tests.
ASTM D698 is a tensile test method, which measures the material’s strength and elongation at break. This test is typically used to evaluate the mechanical properties of plastics, such as their yield strength, tensile strength, and modulus of elasticity.
ASTM D1557 is a flexural test method, which measures the material’s stiffness and resistance to bending. This test is typically used to evaluate the structural properties of plastics, such as their flexural modulus and flexural strength.
Materials and Applications
ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials are used in a wide variety of applications, depending on their specific properties.
When comparing ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557, it’s important to consider the ethical implications of the testing process. The ACA Code of Ethics 2024 provides guidance on conducting ethical research, ensuring that the results are accurate and reliable. By adhering to these ethical principles, researchers can contribute to the advancement of knowledge and understanding in the field of materials testing.
ASTM D698 materials are typically used in applications where strength and toughness are important, such as in automotive parts, appliances, and construction materials.
ASTM D1557 materials are typically used in applications where stiffness and resistance to bending are important, such as in structural components, packaging materials, and medical devices.
Table of Key Properties
The following table compares the key properties of ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials:
| Property | ASTM D698 | ASTM D1557 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | High | Low |
| Elongation at break | High | Low |
| Flexural modulus | Low | High |
| Flexural strength | Low | High |
Manufacturing Processes
The production of ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials involves distinct manufacturing processes, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
ASTM D698 Materials
- Extrusion:Molten plastic is forced through a die to create a continuous shape. This process is efficient and cost-effective for producing large quantities of materials with consistent dimensions.
- Injection Molding:Molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity to create a specific shape. This process allows for complex shapes and high precision, but it can be more expensive and time-consuming.
- Blow Molding:A plastic parison is inflated within a mold to create a hollow shape. This process is suitable for large, lightweight products with intricate designs.
ASTM D1557 Materials, Astm d698 vs astm d1557
- Casting:Molten metal is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify. This process is versatile and allows for complex shapes, but it can result in porosity and surface defects.
- Forging:Metal is heated and shaped by hammering or pressing. This process increases strength and durability, but it is labor-intensive and can be expensive.
- Machining:Metal is cut and shaped using precision tools. This process allows for high accuracy and complex geometries, but it can be time-consuming and generate waste.
Performance Characteristics

The performance characteristics of ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials play a crucial role in determining their suitability for various applications. These characteristics include tensile strength, elongation, tear resistance, and puncture resistance.
Tensile strength refers to the material’s ability to withstand pulling forces, while elongation measures its ability to stretch before breaking. Tear resistance indicates the material’s resistance to tearing, and puncture resistance measures its ability to resist being punctured.
Tensile Strength
ASTM D698 materials generally exhibit higher tensile strength compared to ASTM D1557 materials. This makes them suitable for applications requiring high strength, such as strapping, ropes, and tarpaulins.
Elongation
ASTM D1557 materials typically have higher elongation compared to ASTM D698 materials. This property makes them more flexible and suitable for applications requiring flexibility, such as packaging films and stretch wraps.
Tear Resistance
Both ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials offer good tear resistance, making them suitable for applications where resistance to tearing is crucial, such as bags, sacks, and protective clothing.
Puncture Resistance
ASTM D698 materials generally exhibit higher puncture resistance compared to ASTM D1557 materials. This property makes them suitable for applications requiring protection against punctures, such as puncture-resistant films and puncture-resistant gloves.
| Property | ASTM D698 | ASTM D1557 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Higher | Lower |
| Elongation | Lower | Higher |
| Tear Resistance | Good | Good |
| Puncture Resistance | Higher | Lower |
Testing Methods
Evaluating the properties of ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials requires standardized testing methods to ensure consistent and reliable results. These methods assess various aspects of the materials’ performance and behavior.
Using standardized testing methods is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it enables comparisons between different materials and batches, ensuring quality control and consistency. Secondly, it allows researchers and manufacturers to develop and improve materials based on objective data. Thirdly, it facilitates the exchange of technical information and collaboration among stakeholders in the industry.
ASTM D698 Testing Methods
- Tensile Strength and Elongation:ASTM D638 determines the material’s ability to withstand tension and its elongation before breaking.
- Flexural Strength and Modulus:ASTM D790 evaluates the material’s resistance to bending and its stiffness.
- Impact Strength:ASTM D256 measures the material’s toughness and resistance to impact forces.
- Hardness:ASTM D2240 assesses the material’s resistance to indentation and scratching.
ASTM D1557 Testing Methods
- Tensile Strength and Elongation:ASTM D638 determines the material’s ability to withstand tension and its elongation before breaking.
- Flexural Strength and Modulus:ASTM D790 evaluates the material’s resistance to bending and its stiffness.
- Impact Strength:ASTM D256 measures the material’s toughness and resistance to impact forces.
- Tear Strength:ASTM D1938 assesses the material’s resistance to tearing.
Industry Standards
Industry standards play a crucial role in the production and use of ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials. They establish guidelines and specifications that ensure the quality, safety, and performance of these materials, safeguarding the interests of both manufacturers and consumers.
Adhering to industry standards offers several benefits. It:
- Promotes consistency in product quality and performance
- Facilitates communication and understanding between suppliers and customers
- Reduces the risk of accidents and product failures
- Enhances consumer confidence and trust in products
Relevant Industry Standards
The following are some of the relevant industry standards for ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials:
- ASTM D698
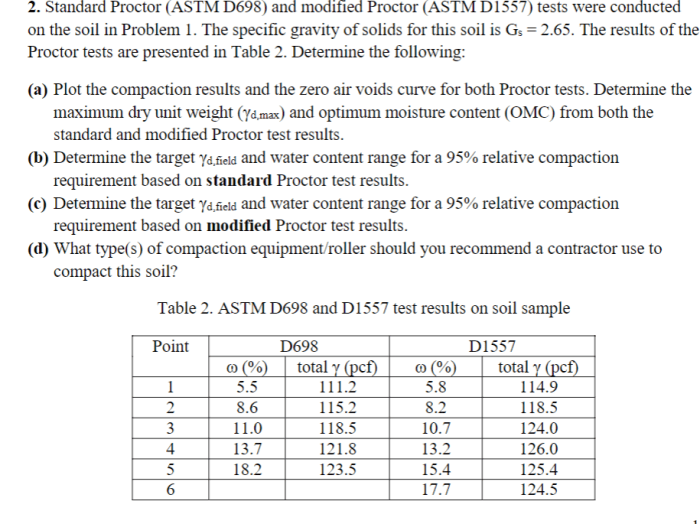
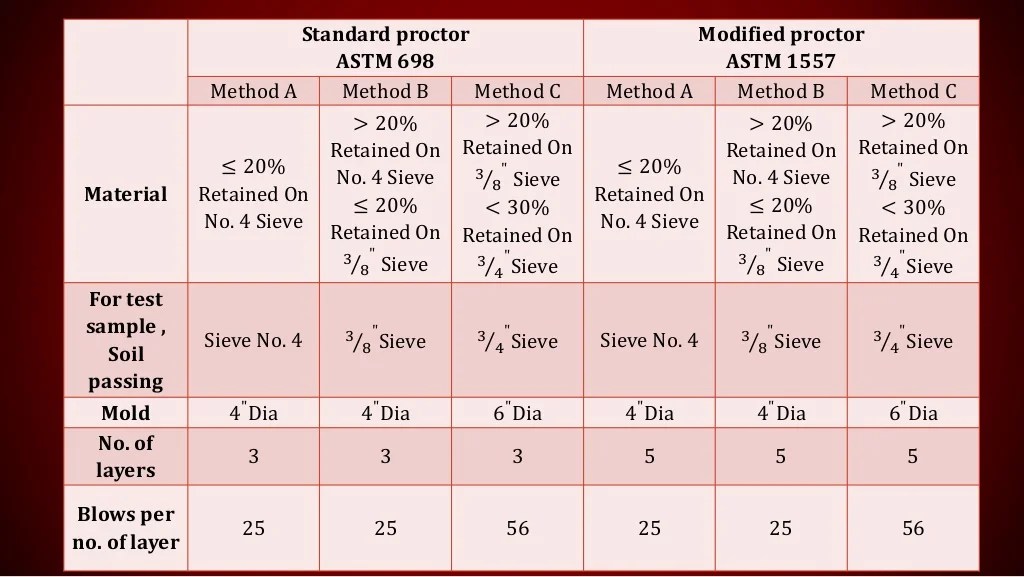
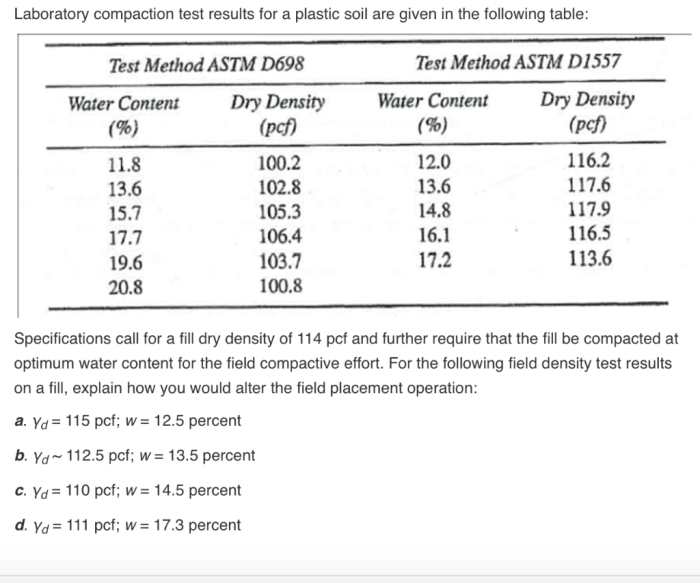
- ASTM D698: Standard Test Method for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12,400 ft-lbf/ft3 (600 kN-m/m3))
- ASTM D698M: Standard Test Method for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Modified Effort (56,000 ft-lbf/ft3 (2,700 kN-m/m3))
- ASTM D1557
- ASTM D1557: Standard Test Method for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Modified Effort (56,000 ft-lbf/ft3 (2,700 kN-m/m3))
Environmental Considerations
ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials have varying environmental impacts throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal. Understanding these impacts and adhering to regulations is crucial for responsible manufacturing and disposal practices.
Production
Producing ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials involves extracting raw materials and processing them through energy-intensive processes. Mining operations for materials like copper and zinc can disrupt ecosystems and pollute water sources. The manufacturing processes also generate greenhouse gases and other emissions that contribute to air pollution.
Disposal
Improper disposal of ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials can harm the environment. These materials may contain hazardous substances that can leach into soil and groundwater if not disposed of properly. Regulations exist to ensure proper disposal methods are followed, such as recycling, landfilling, or incineration under controlled conditions.
Recommendations
To reduce the environmental impact of ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials, consider the following recommendations:
- Use recycled materials whenever possible to reduce the need for raw material extraction.
- Implement energy-efficient manufacturing processes to minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
- Explore biodegradable or recyclable alternatives to reduce the environmental impact of disposal.
- Adhere to all applicable regulations and guidelines for disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
By taking these steps, manufacturers and users can contribute to a more sustainable lifecycle for ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557 materials.
FAQ Summary: Astm D698 Vs Astm D1557
What is the primary difference between ASTM D698 and ASTM D1557?
ASTM D698 is a specification for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) resin used in electrical insulation and sealing applications, while ASTM D1557 is a specification for ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) rubber used in automotive and construction applications.
Which material is more resistant to chemicals?
ASTM D698 (PTFE) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to ASTM D1557 (EPDM).
What are the advantages of using ASTM D1557 over ASTM D698?
ASTM D1557 (EPDM) offers advantages such as flexibility, weather resistance, and low cost compared to ASTM D698 (PTFE).