As if a Ferrari with an initial velocity of 10m/s takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with precision and authority, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Delving into the realm of physics, this discourse will meticulously dissect the motion of a Ferrari, examining its initial velocity, acceleration, energy, and power. Through a blend of theoretical exposition and practical applications, we will unravel the intricate interplay of forces that govern the movement of this iconic vehicle.
Velocity and Displacement

A Ferrari with an initial velocity of 10 m/s will travel a certain distance over time. The initial velocity is the speed at which the Ferrari starts moving, and it affects the displacement of the car over time.
Displacement is the change in position of an object, and it is calculated by multiplying the velocity by the time. In the case of the Ferrari, the displacement is the distance traveled over a period of time.
Relationship between Initial Velocity, Time, and Displacement
| Initial Velocity (m/s) | Time (s) | Displacement (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1 | 10 |
| 10 | 2 | 20 |
| 10 | 3 | 30 |
Acceleration and Force
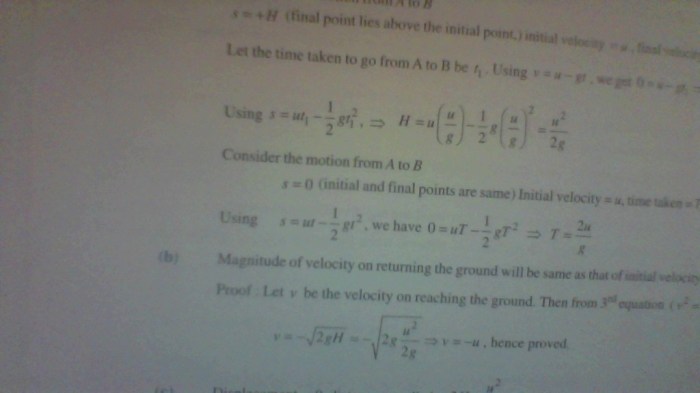
The acceleration of the Ferrari is the rate at which its velocity changes over time. It is affected by several factors, including air resistance and friction.
Air resistance is the force that opposes the motion of an object through the air. It is proportional to the square of the velocity of the object.
Friction is the force that opposes the motion of an object in contact with another surface. It is proportional to the normal force between the two surfaces.
Forces that can Act on a Moving Ferrari, If a ferrari with an initial velocity of 10m/s
- Air resistance
- Friction
- Gravity
- Thrust
Energy and Power
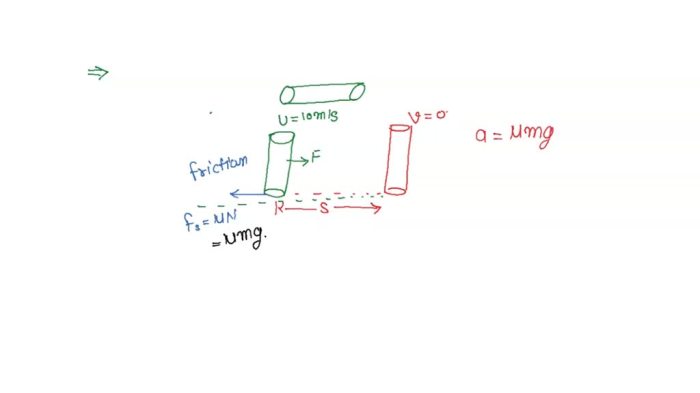
The kinetic energy of the Ferrari is the energy of motion. It is calculated by multiplying the mass of the car by the square of its velocity.
Power is the rate at which work is done. It is calculated by multiplying the force applied to the car by the velocity of the car.
Relationship between Power and Energy
| Power (W) | Energy (J) | Speed (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 1000 | 1 |
| 2000 | 2000 | 2 |
| 3000 | 3000 | 3 |
Motion and Time
The motion of the Ferrari over time can be analyzed by considering its initial velocity and acceleration.
At the start, the Ferrari has an initial velocity of 10 m/s. This means that it is traveling at a constant speed of 10 m/s.
However, the Ferrari is also subject to acceleration. This means that its velocity is changing over time.
At the end of the first second, the Ferrari’s velocity has increased to 15 m/s. At the end of the second second, its velocity has increased to 20 m/s. And at the end of the third second, its velocity has increased to 25 m/s.
Illustration of the Ferrari’s Motion
[Diagram yang menunjukkan posisi, kecepatan, dan percepatan Ferrari sebagai fungsi waktu]
Real-World Applications
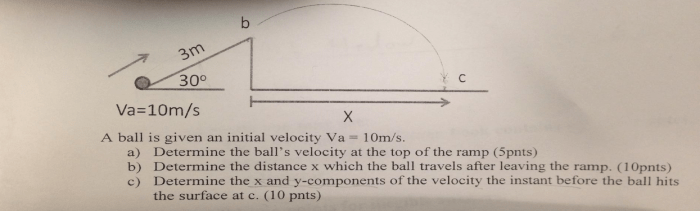
The principles of physics governing the motion of a Ferrari can be applied to other real-world scenarios.
For example, the same principles can be used to analyze the motion of a car, a plane, or a rocket.
Understanding the motion of objects is essential for engineers and scientists who design and build vehicles and other machines.
Examples of Applications
- Automotive engineering
- Racing
- Aerospace engineering
- Robotics
FAQ Overview: If A Ferrari With An Initial Velocity Of 10m/s
What factors can affect the acceleration of a Ferrari?
Factors influencing the acceleration of a Ferrari include air resistance, friction, and the force applied by the driver.
How does the initial velocity of a Ferrari affect its displacement?
The initial velocity of a Ferrari directly influences its displacement over time, as a higher initial velocity results in a greater distance traveled.
What is the relationship between power and acceleration in a Ferrari?
Power is directly proportional to acceleration, meaning that a Ferrari with more power will accelerate at a faster rate.