Embark on a comprehensive exploration of ACLS sepsis HESI case study, where we unravel the complexities of sepsis, its clinical manifestations, and the crucial role of healthcare professionals in its management. Dive into a detailed case study to gain practical insights into patient presentation, diagnosis, and treatment strategies.
Our journey begins with understanding the pathophysiology of sepsis, its clinical manifestations, and the essential management guidelines Artikeld by the Surviving Sepsis Campaign. We will examine the use of HES in sepsis management, weighing its benefits and risks based on evidence-based recommendations.
ACLS Sepsis

Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection damages its own tissues and organs. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Pathophysiology of Sepsis
Sepsis is caused by an overwhelming inflammatory response to an infection. This response can lead to widespread tissue damage, organ failure, and even death. The inflammatory response is triggered by the release of cytokines, which are proteins that signal the immune system to attack the infection.
However, in sepsis, the inflammatory response becomes excessive and damages healthy tissues.
Clinical Manifestations of Sepsis
The clinical manifestations of sepsis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. However, some common symptoms include:
- Fever or chills
- Rapid heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Low blood pressure
- Confusion or disorientation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Skin rash
Management of Sepsis, Acls sepsis hesi case study
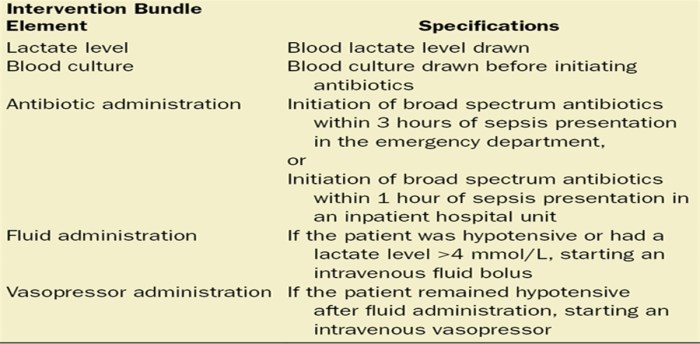
The management of sepsis is based on the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines. These guidelines recommend early recognition and treatment of sepsis to improve outcomes. The key elements of sepsis management include:
- Early identification and diagnosis
- Aggressive fluid resuscitation
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Vasopressors to support blood pressure
- Inotropic agents to support heart function
- Mechanical ventilation
- Source control, which involves identifying and treating the source of infection
Sepsis Case Study
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection damages its own tissues and organs. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to improve the chances of survival.
This case study presents a detailed account of a patient with sepsis, including their presentation, diagnosis, management, and an analysis of the care provided.
The ACLS Sepsis HESI case study is an important resource for nurses who want to improve their understanding of this life-threatening condition. If you’re also interested in improving your consumer math skills, check out the Abeka Consumer Math Test 12 . This comprehensive test can help you identify areas where you need to improve, so you can become a more confident and knowledgeable consumer.
The ACLS Sepsis HESI case study is a valuable tool for nurses who want to provide the best possible care to their patients.
Patient Presentation
The patient is a 65-year-old male with a history of diabetes and hypertension. He presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of fever, chills, and confusion. On examination, he is found to be hypotensive, tachycardic, and tachypneic. His skin is warm and flushed, and he has decreased capillary refill time.
Diagnosis
Based on the patient’s presentation and vital signs, the emergency physician suspects sepsis. A blood culture is drawn, and the patient is started on intravenous fluids and antibiotics.
Management
The patient is admitted to the intensive care unit and placed on mechanical ventilation. He is given vasopressors to support his blood pressure and antibiotics to treat the infection. The patient’s condition initially improves, but he later develops acute kidney failure and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Analysis of Care
The care provided to the patient was timely and appropriate. The emergency physician recognized the signs and symptoms of sepsis and initiated treatment promptly. The patient was given appropriate antibiotics and fluids, and he was placed on mechanical ventilation when his condition worsened.
However, there were some areas where the care could have been improved. The patient’s blood culture was not drawn until after he had been started on antibiotics, which may have delayed the identification of the causative organism. Additionally, the patient was not given steroids, which may have helped to improve his blood pressure and reduce his risk of organ failure.
Overall, the care provided to the patient was good, but there were some areas where it could have been improved. Early recognition and treatment of sepsis is essential to improve the chances of survival.
HESI Sepsis: Acls Sepsis Hesi Case Study
Hydroxyethyl starch (HES) is a type of colloid that has been used in the management of sepsis. It is thought to improve fluid resuscitation by increasing intravascular volume and reducing capillary leak. HES has also been shown to have some anti-inflammatory properties.
Benefits of HES in Sepsis
- Improved fluid resuscitation
- Reduced capillary leak
- Anti-inflammatory properties
Risks of HES in Sepsis
- Increased risk of bleeding
- Increased risk of renal failure
- Increased risk of allergic reactions
Evidence-Based Recommendations for the Use of HES in Sepsis
The use of HES in sepsis is controversial. Some studies have shown that HES can improve outcomes, while other studies have shown that it can increase the risk of adverse events. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines recommend that HES should not be used in patients with sepsis.
Nursing Care for Sepsis
Nurses play a pivotal role in the care of patients with sepsis, as they are often the first healthcare professionals to encounter and assess patients with suspected sepsis. Nurses are responsible for initiating early recognition and intervention, as well as providing ongoing care and support throughout the patient’s journey.
Key Nursing Interventions
Key nursing interventions for the prevention and management of sepsis include:
- Early recognition and assessment:Nurses assess patients for signs and symptoms of sepsis, such as fever, chills, hypotension, and altered mental status.
- Prompt initiation of antibiotics:Nurses administer antibiotics as soon as possible after sepsis is suspected, as early administration improves patient outcomes.
- Fluid resuscitation:Nurses provide intravenous fluids to maintain adequate blood pressure and tissue perfusion.
- Vasopressor administration:Nurses may administer vasopressors to increase blood pressure if fluid resuscitation alone is insufficient.
- Source control:Nurses assist with identifying and treating the source of infection, such as draining abscesses or removing infected devices.
- Monitoring and evaluation:Nurses closely monitor patients with sepsis for changes in vital signs, fluid balance, and laboratory values.
- Patient and family education:Nurses provide education to patients and their families about sepsis, its symptoms, and treatment.
Nursing Care Plans
Nursing care plans for patients with sepsis are individualized based on the patient’s condition and response to treatment. However, some common elements of a nursing care plan for sepsis include:
- Assessment:Assessment of vital signs, fluid balance, laboratory values, and mental status.
- Interventions:Administration of antibiotics, fluid resuscitation, vasopressor administration, source control, and monitoring.
- Monitoring:Close monitoring of patient response to treatment, including vital signs, fluid balance, and laboratory values.
- Education:Education of the patient and family about sepsis, its symptoms, and treatment.
- Evaluation:Evaluation of the patient’s response to treatment and adjustment of the care plan as needed.
FAQ Resource
What are the key clinical manifestations of sepsis?
Sepsis presents with a range of clinical manifestations, including fever, chills, tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, and altered mental status.
How does HES contribute to sepsis management?
HES acts as a volume expander, increasing circulating blood volume and improving tissue perfusion in patients with sepsis.
What is the role of nurses in sepsis care?
Nurses play a pivotal role in sepsis care, providing early recognition, implementing timely interventions, monitoring patient response, and educating patients and families.